The Arctic
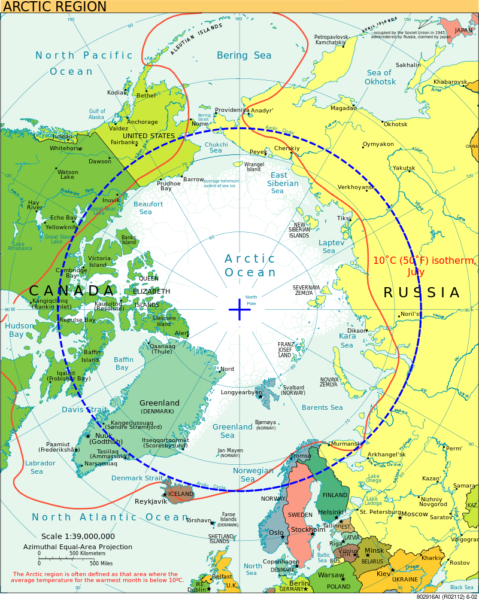
Polar Bears are ONLY found in the Arctic. The Artic is the northernmost part of Earth and is home of the North Pole. This region is an ocean, guarded by a layer of perpetual sea ice. It is surrounded by parts of the United States (Alaska), Finland, Greenland, Iceland, Northern Canada, Norway, Russia, and Sweden. Water enters the Arctic Circle from both the Pacific and the Atlantic Oceans. The region is around 14.5 million square km (5.5 million square miles) in size.
Polar Bears
Polar bears live on the thick sea ice, developed by the regions extremely cold temperatures, as well as the surrounding land. Contrary to popular belief, you cannot find polar bears in Antarctica. They only reside in the Arctic. However, you would find penguins in the southern polar region!
Size & Weight
Cub
Polar bear cubs are born at around 2 pounds and are about 30cm in length, males being slightly larger than females. Before the babies leave their den, they can gain over 30 pounds. A cub needs to put on 100 times its birthweight by the time mama leaves its baby, around two and a half years. Only around 50% will survive.
Size & Weight
Adult
An adult male polar bear may reach more than 10 feet tall when standing on their hind legs and weigh up to 1,500 pounds – record male shot in Alaska (1960) weighed 2,210 pounds and stood 12 feet tall. Female polar bears can be two to three times smaller than males. Females are generally 6-8 feet tall and weigh up to 1,000 pounds.
Polar bears are physically the largest species of bear.
Are Polar Bears White?
Adult
While Polar Bears look white, interestingly enough, their fur has no white pigment and their skin is actually black. The hairs on polar bears are actually hollow, however, their thickness allows polar bears to appear white and blend in with their Arctic surroundings. Their coat provides such great camouflage, that they sometimes are mistaken for a snow drift. Their black skin, thick coat, and thick layer of body fat helps them stay warm in freezing conditions.
Cub
Young cubs have thin fur and rely heavily on mama to keep warm. As newborns, they appear hairless because their fur is so fine.

Polar Bear Paws
Polar bear paws are four times the size of human hands, averaging around 12 inches in size. Their paws are crucial to their survival as their mass provides added traction on the ice as well as stabilizing their weight. Their large paw disperses their weight out over deep snow and thin ice to avoid falling through. A polar bear’s paw has thick, black covered pads with soft papillae. Papillae are dermal bumps that enhance friction between ice and paw to prevent slipping. Slipping is also prevented by the long hairs that are dispersed between their toes.
Polar Bear Facts:
Did you know polar bears are the largest species of bear?
Diet
General Overview
Being the world’s largest species of bear, polar bears need to eat massive amounts to satisfy their enormous physique. They are carnivores, meaning they eat meat, but they will occasionally eat plants and berries. Their main sources of protein include seals, walruses, and beluga whales. They have a high fat diet and rely on their prey as a source of water since most of the drinkable water is frozen. When food sources are scarce, polar bears will turn to any animal they can prey off of, including rodents, reindeer, or seabirds.
Interestingly enough, polar bears do not catch and eat fish, as most Arctic fish swim at very deep depths and polar bears are not divers.
Seals
Polar Bears are the most carnivorous member of the bear species. Their stomachs can hold 15-20% of its total body weight to prepare for hibernating when they don’t eat anything at all. A polar bear can go 8 full days without eating if they consume a seal weighing 121 pounds. Their diet consists mainly of ringed and bearded seals, occasionally consuming harp, hooded, or ribbon seals. They kill up to 44% of all newborn seals every year.
Others
Along with consuming seals and their young, polar bears will basically eat any carcass that they can find. This includes beluga whales, grey whales, bowhead whales, walruses, and narwhals. They feed on the carcasses because polar bears cannot attack these large animals. When food is scarce or unavailable, they will consume seabirds, fish, eggs, vegetation, berries, and human garbage.

A Harp Seal, which is NOT a species of seal that polar bears consume.
Photo Captured by Thomas Kokta
Random Polar Bear Facts:
Polar bears can reach speeds up to 40 kph
(25 mph) on land and 10 kph (6 mph) in water.
Social Behavior
There are two social units between polar bears: breeding pairs and mama & cub.
Breeding Pairs
During mating season, breeding pairs stay together for several weeks. Mates are usually found between late March to June. After females find their partner, the pair will mate several times. It is not uncommon for male polar bears to become aggressive toward other males throughout breeding season. Most adult females give birth once every three years, occasionally every two years if the bears have access to large quantities of food.
Mama & Cub
The highest level of social interaction is between the females and their cubs. This is because polar bear mothers are very attentive to their babies. Polar bear babies need large amounts of attention, including snuggle warmth, feeding, cleaning, etc. Females can have up to three cubs at one time. Mama and baby stay together for around two and a half years before the mother leaves the cub to discover the world on its own. During those two and a half years the cub is taught the ways of survival, such as identifying scents, hunting, and sheltering, in order to ensure survival after mama leaves.
Hunting
Aquatic Prey
The most common method of hunting polar bears practice is Still Hunting. This is when a polar bear waits on the edge of ice and remain motionless as they wait for their prey, usually a seal, to surface. They will catch the seal by its head or upper body, then pull the entire seal onto the surface of the ice. Another common hunting method for aquatic prey is called Aquatic Stalk. Aquatic stalk is when a polar bear swims to a piece of sea ice and emerges from the water quickly to grab its prey. After capture, they disable the seal by biting it several times in the head and neck. They eat the skin and blubber first, then the meat, only to leave behind a few scraps.
Land Prey
Stalking is a common hunting method polar bears use to capture food on land. This happens when a polar bear spots a seal and follows them from 15 to 30 meters away. They then charge at the seal and captures it before they can return to the Arctic water. When a mama and cub are together, their most used method of hunting is Stalking Birth Lairs. These birth lairs are attached to land and are where seal pups reside. Mama and cubs use this hunting method because it avoids the crossing of water as well as baby interaction with any male polar bears since male polar bears do not hunt birth lairs.
Polar Bear Development
Pregnancy
Once a female has mated, she will need to gain at least 440 pounds so she can carry out a successful pregnancy. Between August and October, Mothers will spend their pregnancy in search for an area to build a den to keep their newborns protected from the harsh outside temperatures. Birthing season is anywhere from November to January. They are born with their eyes closed, but they open within a month. They also have very fine hair at birth, so they rely heavily on mother for warmth.
Early Months
During the early months, cubs never leave their mom’s side because they’re always nursing or needing warmth. A baby nurses up to six times a day. A few months after their birth, typically March or April, mothers will begin exposing cubs to new environments. This exposure comes after the baby has adapted to cold temperatures and developed enough muscle to walk. After the first exposure, mama and baby will continue to utilize the den for several days until the baby is prepared to leave.
Growing Up
They eventually leave their den so the cub can be taught how to hunt and eat solid foods from their mother’s kill. A baby’s success rate for hunting is low for their first year. Baby polar bears should reach around 100 pounds by the time they reach eight months of age. As the baby learns how to hunt and eat they will put on over 300 pounds, weighing around 400 pounds by two years. When a cub reaches the 30 month old marker, the polar bear mother is ready to leave baby. During this point, the cub is challenged to test all the skills they have been taught to survive on their own.
Daily Activity
Polar Bears are most active in the mornings. Their energy steadily depletes as the day falls into evening. Females and cubs hunt 19% of the day during spring season, and 38% of the day during the summer months. Males hunt for a quarter of their day in the spring, and 40% during the summer. When polar bears are not hunting, they spend the majority of their day sleeping and resting. During warmer, sunny days, they will make snow pits to lay in, or just lay out without a pit to soak up the warmth of the sun. During colder, cloudier days, polar bears will find shelter to utilize for several months, depending on the severity of the winter.
Why Do Polar Bears Need Our Help?
The polar bear is the world’s largest terrestrial carnivore and spends most of its life in the water or on Arctic sea ice. Their health helps researchers understand the status of the Arctic. Polar bears are often used as gauges when identifying the health of the whole polar region because they are at the top of the food chain.
Decrease in Polar Bear Population (by 2050)
Polar Bear Threats
Climate Change
What is it?
Climate change is the adjustment of the Earth’s global or regional environment over time. This could be global warming or global cooling. Global warming meaning regional temperatures have rose, while global cooling means regional temperatures have fallen. Climate change is especially concerning for colder areas, such as the Arctic.
How does it affect Polar Bears?
This affects polar bears in devastating ways. Arctic temperatures are rising two times as quickly as the global average. Because of this, sea ice coverage is shrinking by nearly 4% per decade. Studies have shown that this has affected polar bears’ ability to find food. Warmed up temperatures kickstart summer seasons earlier and earlier each year, resulting in early melting of the ice. This leaves the bears with a smaller window of which to find food.
Polar bears will NOT be able to overcome the impacts of global warming on their cold-driven territory. According to researchers, polar bears cannot adapt their metabolisms to survive on land-based prey during longer and longer periods with no sea ice.
Impact on Cubs
When polar bears do not have a sufficient supply of food, they are unable to reproduce at normal rates. As sad as it is, cubs are often killed as a result of mama needing food. Cubs may also die of starvation. Global warming has led to an increase in baby mortality, which can lead up to extinction. It is estimated that polar bears may potentially face complete starvation and reproductive failure by 2100.
Seismic Testing
What is it?
Seismic testing is the process of seeking oil and gas reserves by use of cosmic torrents of sound. Using strong air guns, testers have the ability to penetrate the ocean floor. This allows testers to gather data about what lies beneath the surface. Blasts are as frequent as every 10 seconds for as long as months at a time. This has the potential to devastate marine life. For the Arctic, seismic testing would take place on the coastal plain and would involve large heavy trucks to drive across the tundra.
How does it affect Polar Bears?
The equipment that is used will disrupt the area with vibrating and significant magnitudes of hemorrhage-inducing noises. The private company that is conducting the seismic testing in the Arctic promises to distinguish any polar bear dens prior to starting the testing, however, there is no guarantee of 100% distinction before beginning testing. Specialists have also claimed that there is no guarantee that any polar bears will NOT be harmed or even killed.
Impact on Cubs
Mothers may abort from the den too early, exposing their young to elements they are not yet prepared for, when they are disturbed. When a cub is denning, they rely on their mom and the den to keep them warm, without the den, they will likely freeze to death. A mother may also abandon their young completely when startled.
Scientists have determined there is a one-in-four chance that seismic equipment will run over at least on den. This was concluded because of the amount and size of equipment necessary to perform seismic testing and the known concentration of polar bear dens in the region.
Toxic Pollution
What is it?
Toxic pollution is harmful or poisonous water, soil, or air. Toxic pollutants are physical materials that contaminate our environment, causing death, disease, or birth defects of those exposed. Sources of these pollutants include coal-fired power plants, industries, refineries, tobacco smoke cars, trucks, and basically anything that emits toxic gas.
How does it affect Polar Bears?
Toxins are pumped through animals’ bodies when they are exposed to pollution. This poses issues for polar bears because their food is infecting them. The Arctic food chain reveals high levels of various toxic chemicals, contaminating the polar bear’s diet. Their thyroid hormones, vitamin A levels, and antibody levels are impacted after being exposed to POPs (persistent organic pollutants) at high levels. Polar bears’ reproduction, growth, and ability to fight off diseases are a negative consequence of these pollutants.
Impact on Cubs
Polar bear mama’s hold the highest levels of POPs researchers have ever seen. Milk with these chemicals will poison cubs, causing lower cub survival rates.
Oil Exploration
What is it?
Oil exploration, also known as hydrocarbon exploration, is the portion of the petroleum industry that is responsible for exploring new crude oil and gas fields. Petroleum geologists and geophysicists drill wells in the earth and collect material below the surface. This practice expanded across various regions, including the Arctic.
How does it affect Polar Bears?
This poses great risks to polar bear populations if the process were to have any disruptions. Offshore operations risk spills, leaks, regular emissions, and chemicals being drained into the ocean or on sea ice. Oil spills cause a reduced insolated effect of polar bears’ fur. These spills often contaminate polar bear prey, causing an issue upon ingestion. Ingestion causes kidney damage, liver damage, and other long-term harms. Along with the negative impact of oil leakage, the process itself can cause disturbance and destruction of habitat.
Polar Bear Facts
When is Polar Bear day?
February 27th
How big is the largest Polar Bear?
The largest polar bear in the record was a grown male that had 2,209 pounds.
How do Polar Bears communicate?
Sight, touch, and smell are main forms of communication among polar bears. Mothers often warn their young with a chuffing or braying sound. When a male lurks its head down, their mouth is closed and eyes averted, that means another male is approaching.
What color are Polar Bears?
They appear white, but they actually have black skin and translucent fur. Their fur only looks white because it reflects light to help them blend in with their surroundings.
How well can a Polar Bear Smell?
Polar bears can smell scents from extremely far away. Up to 20 miles away
How do Polar Bears dry their fur?
When they came up to the ice, they first shake off the water in the fur, and roll in the snow like a towel and dry the fur off.
How far can Polar Bears swim?
They can hunt under the sea ice and they can swim as much as 60 miles without any rest. But because of global warming and decline of glaciers, polar bears need to swim increasingly father away to find a place to stop. With less sea ice, it is not uncommon for a polar bear to drown from swimming from ice to ice.
Are Polar Bears endangered?
Unfortunately, they are heading in that direction. Because of global warming, ice caps continue to melt – negatively impacting the polar bear population.The population of polar bears is expected to decline by 30% by 2050.
Can we save Polar Bears?
Yes! We can contribute to the health of our furry friends. Since polar bears have been classified as threatened species under the Endangered Species Act (ESA), more and more people have donated to research on polar bear survival. The Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA) partners with various organizations to help protect polar bears and their habitats through research, education, and conservation efforts. AZA-accredited facilities are leaders in animal welfare, saving species and endangered species conservation. Through our Saving Animals From Extinction (SAFE), Species Survival Plans (SSPs), and Wildlife Trafficking Alliance (WTA) programs/partnerships we are helping to spread awareness about species like the polar bear.